41 dosage calculations with labels
Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method The answer seems plausible, so the work is done. 1000/500 x 10/5 = 2, the 2 zeros in 1000 and 2 zeros in 500 can be crossed out since like units in numerator and denominator, leaving 10/5, a much easier fraction to solve, and the answer makes sense. If you multiply a number by a 1, then the number is unchanged. Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA
Oral Drug Dosage Calculator - Liquid Solution Syrup × Q (quantity) X (amount) = 500 milligram 250 milligram ×5 milliliter X (amount) =10 milliliter Description: This calculator determines the volume of liquid, solution or syrup to be administered to the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine.
Dosage calculations with labels
Delmar Cengage Learning Companions - Math for Meds, Dosages and Solutions Chapter 9: Parenteral Medication Labels and Dosage Calculation / 104; Chapter 10: Reconstitution of Powdered Drugs / 126; Chapter 11: Measuring Insulin Dosages / 142; SECTION 4: DOSAGE CALCULATIONS; Chapter 12: Ratio and Proportion / 164; Chapter 13: Dimensional Analysis / Units Conversion / 196; PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Southwest Tech Math/Science Center 3.27K subscribers Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters...
Dosage calculations with labels. Dosage Calculations the Easy Way! - Straight A Nursing Everything except for tablets is crossed out, so we know we are ready to do some math. 1) Multiply across the top: 650 x 1. 2) Then divide across the bottom: ÷ 325. What answer did you get? Let's do one more easy one…. For this calculation, let's assume midazolam comes in 5 mg tablets. Dosage (Drug) Calculations Nursing Review- COMPREHENSIVE This is a comprehensive dosage calculation review for nursing students. In this review we will start by working basic metric conversions and then progress to solving more complex dosage calculations. You will learn how to work the following drug calculation problems: Conversions Oral Liquid Medications Capsules and Tablets IV Boluses Medical Dosage Calculations For Dummies Cheat Sheet Common conversion factors in medical dosage calculations. As a healthcare professional, you have to convert patient weights, fluid volumes, medication weights, and more. Conversion math isn't hard to do as long as you know the basic conversion factors. Here are the most useful ones: Converting lb to kg and kg to lb. lb = kg × 2.2. kg = lb ÷ 2.2 LibGuides: Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and ... The dosage strength of the reconstituted medication will be specified on the label. The dosage strength of the reconstituted medication is the strength the nurse will use in calculating the amount of medication to give the client according to the healthcare provider's prescription.
Dosage Calculation - Label Reading | Other - Quizizz Play this game to review Other. What is the dosage strength? Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Quiz. Dosage Calculation - Label Reading. DRAFT. 10th - University. Played 414 times. 72% average accuracy. Other, Life Skills. 6 months ago by. shelley_dinkens_86955. 3. Save. Edit. Edit. Dosage Calculation - Label Reading DRAFT. 6 months ago by. shelley ... Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 2: On the right side, place the information given with the same label needed in the numerator. In this example, we know that the drug concentration available is 0.25 mg/mL. Place mL in the numerator and 0.25 mg in the denominator. Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into ... Pharmacy Dosage Calculations - Pharmacy Tech Review First, note that both grams and milligrams are used in the problem so we need to do a measurement conversion. There are 1,000 milligrams per gram. The first ratio is one dose per 20mg so ¹⁄₂₀. The second ratio contains an unknown so initially it is ˣ⁄₁₀₀₀. Set these two ratios in a proportion. Dosage Proportion With Unknown. PDF Drug Calculation tutorial - Midlands Tech Drug labels obtained from Bing Label Images. 3 MIDLANDS TECHNICAL COLLEGE NURSING DEPARTMENT DO NOT USE LIST Appropriate PROHIBITED Abbreviation or Alternative ... Dimensional analysis is the method of drug calculations that is taught in MTC's Nursing Program. Evidence has shown that dimensional analysis is the safest and quickest method of ...
Nursing Pharmacology: Dosage And Calculations Practice Test - RN speak The medication label reads "1,200,000 units per 2 mL." The nurse has determined that the dose prescribed is safe. The nurse administers how many milliliters per dose to the child? a. 0.8 mL b. 1.2 mL c. 1.4 mL d. 1.7 mL 19. Atropine sulfate, 0.6 mg intramuscularly, is prescribed for a child preoperatively. Calculating from the labels | Learning Lab This short video is the second of three videos in the Nursing calculations - Finding the volume required section. It explains how to calculate medication dosage from labels using the method of mental calculation and proportinality to get the right dosage for drugs in solution. Transcript Worksheet (ZIP) Activity 1 » Keywords: Nursing Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? Let's say the appropriate dosage of the active substance is 2 mg/kg of body weight. Weigh yourself. Let's assume you weigh 80 kg. Multiply these two values to get the dose of medication in mg: 2 * 80 = 160 mg. You need to take 160 mg of active substance. What if your medication is liquid? Type the concentration into the proper box. Pharmacy Dosage Calculations | Pharmacy Math Made Simple! - PharmaFactz 0.5mg x 1,000 = 500 micrograms. Adrenaline is available as an injection of 100 micrograms/mL. Therefore we need 5mLof the available adrenaline formulation. Answer: 5mL Sample Problem 5 The recommended dose of fluconazole for mucosal candidiasis in children is 3mg/kg daily. Calculate the dose needed for a child (3-years old).
Dosage Calculations Nursing Comprehensive Quiz - Registered Nurse RN Dosage Calculations Nursing Practice Quiz Questions 1.) 27 mg= mcg * A. 270 mcg B. 27,000 mcg C. 0.027 mcg D. 37 mcg 2.) 6 tsp = ml * A. 5 mL B. 1.5 mL C. 30 mL D. 15 mL 3.) The doctor writes an order for a liquid oral medication. The order says to administer 15 mg by mouth every 4 hours as needed for sore throat.
PDF Drug dosage calculation handout for BSN completion 16. The provider orders 125mg of amoxicillin Q. 8 hrs. for a patient weighing 58 lbs. Calculate the daily dosage range recommended on the label and compare the daily dose ordered by the doctor. Does the provider order fall within the usual dosage range? 17. Aggrastat is ordered to infuse at 0.1 mcg/kg/min for a patient weighing 136 lbs. A ...
ATI Dosage Calculations 3.0: Oral Medications - Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A nurse is preparing to administer methadone 2.5 mg PO every 8 hr. Available is methadone 5 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer per dose?, A nurse is preparing to administer quinapril 40 mg PO daily. Available is quinapril 20 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer daily?, A nurse is ...
Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - StuDocu Dosage Calculation: Reading Drug Labels Chapter 11. Tarleton State University NURS 3310 Dr. Mary B. Winton. Reading Drug Labels. a. Brand/trade name b. Generic name c. Formulation d. Dosage strength e. Route f. Need prescription or Over -the-counter. Reading Drug Labels and Reconstitution. a. Generic name b. Brand/trade name c. Formulation d ...
Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide - KnowledgeDose The available stock is 2000 units/ml. The pharmacist has asked the pre-registration pharmacist to also state how many mls of colecalciferol Mr X should take on the dispensing label. What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily
Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College First attempt—week of September 12-15, 2022. Option A: In person (paper exam) Thursday, September 15, 2022. 5:00 pm to 7:00 pm. Room 105, Health Sciences Building. Decatur Campus. Option B: In the Testing Center (computer exam) Sept 12 - 15, 2022 at your convenience for $13.50. Locations at Decatur and Huntsville Campuses.
Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Every tenth of a mLis marked on the syringe, and every half mL is labeled; this means that any dosage we plan to measure using a 3 mL syringe should be rounded to the nearest tenth. Dosages between 1-3 mLshould always be measured in a 3 mL syringe.
Dosage Calculation Practice_Reading Labels.pdf - Dosage... Calculations (12-14) answers. 12) Number of of emtricitabine tablet required. Ordered dose = 200 mg. Available dose = 100 mg/tab. Number of tab required = 200/100 = 2 tablets. 13) ml of drug required. Volume (ml) = Desired dose/Dose in hand *Quantity. Here Desired dose = 600 mg. Dose in hand = 400 mg. Quantity = 1 ml. As per above formula
Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN - Registered nursing Calculating Oral Medication Dosages Using Ratio and Proportion. Here is an example of how to calculate oral medication dosage using ratio and proportion: Doctor's order: 125 mg of medication once a day. Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg. How many tablets should be administered daily?
Dosage Calculations- Chapter 8: Understanding drug labels - Quizlet Start studying Dosage Calculations- Chapter 8: Understanding drug labels. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Dosage and Calculations Math Practice - StuDocu Any of the following thr ee methods can be used to perform drug calculations. Pl ease. re view all thre e methods and select the one that works for you. It is important to ... H = dose on container label or d ose on hand . V = form and amou nt in which drug comes (tablet, capsule, liquid) Example: Order-Dilantin 50 mg po TID.
Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Southwest Tech Math/Science Center 3.27K subscribers Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters...
PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration
Delmar Cengage Learning Companions - Math for Meds, Dosages and Solutions Chapter 9: Parenteral Medication Labels and Dosage Calculation / 104; Chapter 10: Reconstitution of Powdered Drugs / 126; Chapter 11: Measuring Insulin Dosages / 142; SECTION 4: DOSAGE CALCULATIONS; Chapter 12: Ratio and Proportion / 164; Chapter 13: Dimensional Analysis / Units Conversion / 196;






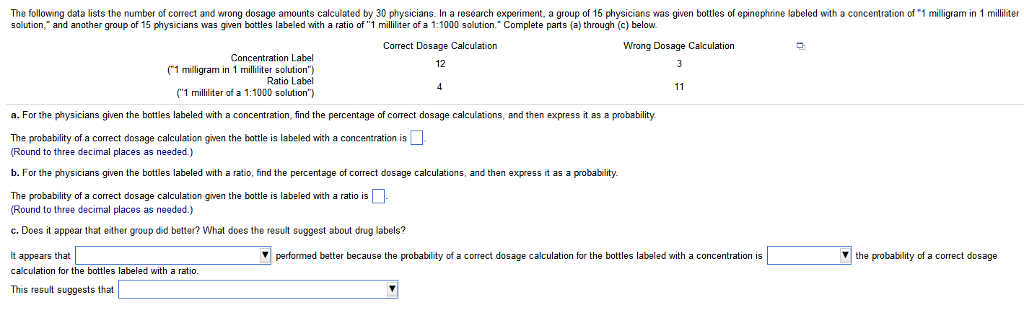












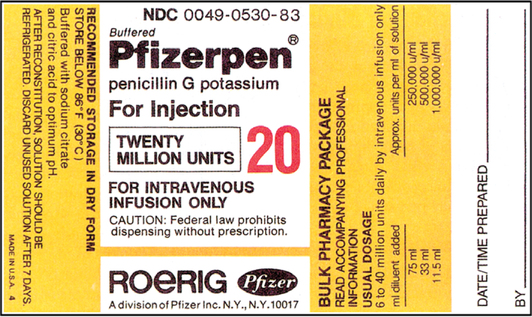



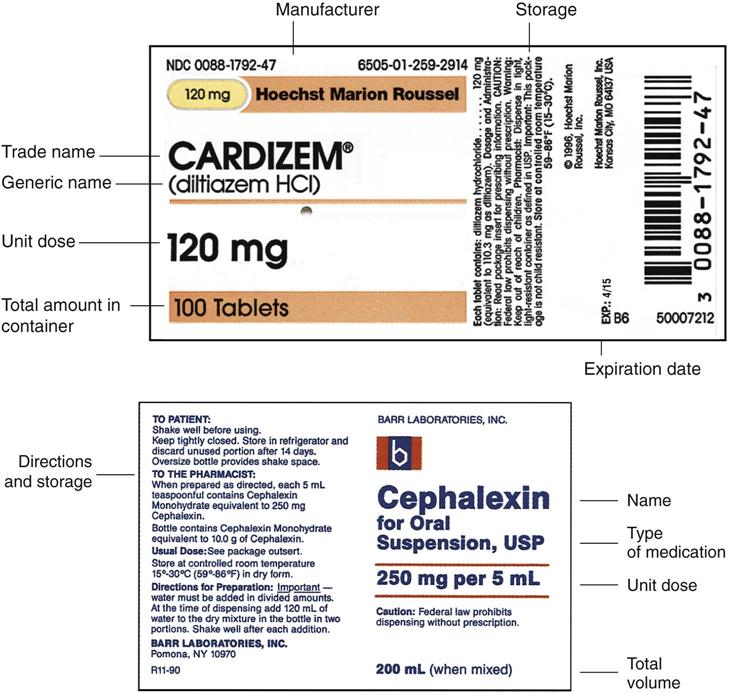



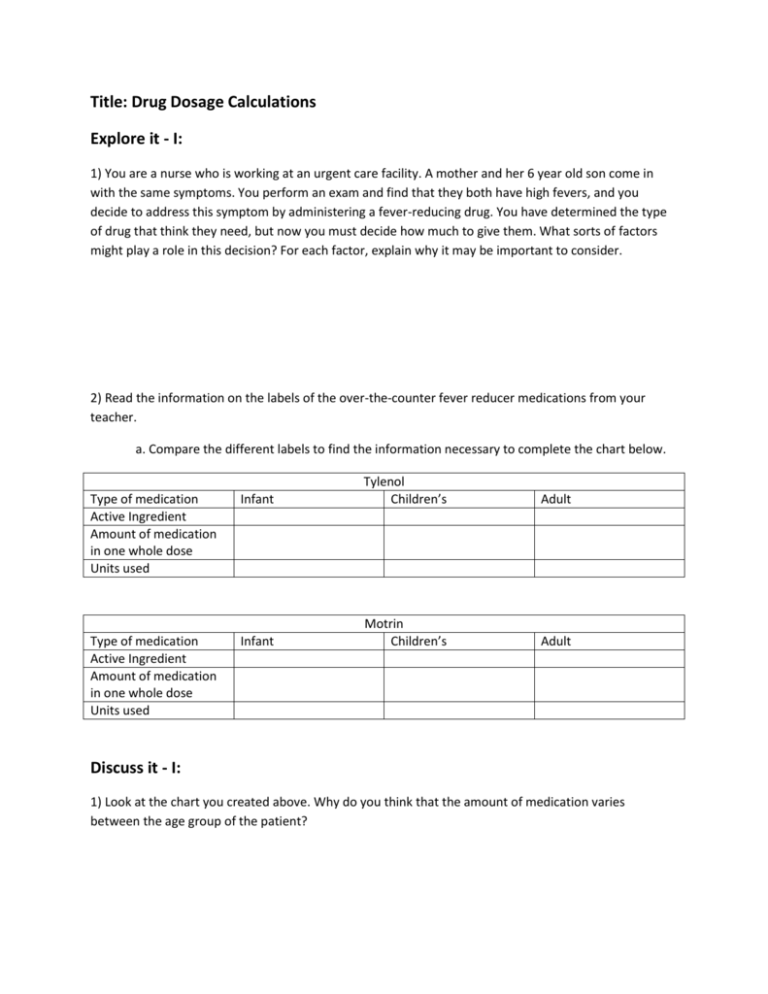


Post a Comment for "41 dosage calculations with labels"